Wifi Radar
Wifi Radar is application which create map based on Wifi signal strength
Project maintained by korsumaki Hosted on GitHub Pages — Theme by mattgraham
Wifi Radar
Brief
Wifi Radar is (experimental) application to scan WiFi access points and create map about those.
Secondary purpose for this application is to learn more Kotlin, Jetpack Compose and Android application development.
Description
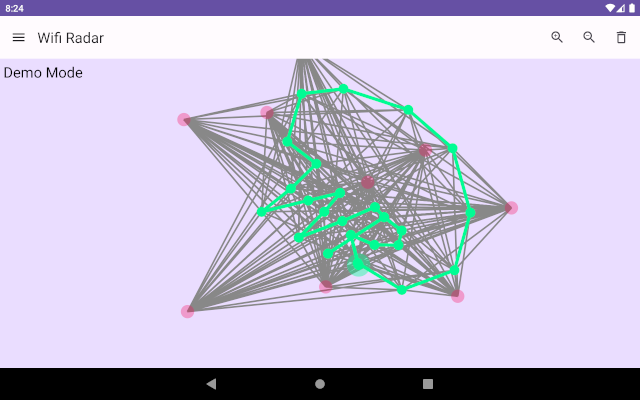
Wifi Radar calculate estimated distance to WiFi access points (AP) based on signal levels. It will create relative map around APs and user locations. Map does not have any other relations to real world than those APs.
Scanned AP data is given to ForceGraph data structure, which create spring-like relations between AP’s and current scanning position. Then ForceGraph calculate spring forces for relations, and let APs to move around by pushing and pulling each others.
After while, with enough scanned APs and enough different scanning positions, map start to get its shape to show how APs relate to each other, and where user is within those.
Note that ForceGraph cannot separate left and right, or which direction is forward. When compared to real world, map can be mirrored and pointing to different direction on screen.
Map creation algorithm (more detailed description)
Actual map creation is done with ForceGraph data structure.
ForceGraph
ForceGraph data structure contain ForceNodes and ForceRelations.
ForceRelation is spring with target length and spring constant. It is always connecting exactly two ForceNodes. If ForceRelation’s actual length differs from target length, it is causing spring force between ForceNodes it connects.
ForceNode is point which have location, mass and velocity. It is connected to other ForceNodes with one or more ForceRelations. All ForceNode’s ForceRelations’ spring forces are calculated together to sum force vector. ForceNode’s sum force vector will cause acceleration, which change velocity, which change location.
ForceGraph is iterating continuously by calculating:
- Spring force (based on ForceRelation’s length)
- Acceleration
- New velocity
- New location
- Changed locations are changing ForceRelation’s length, so go back to step 1.
Wifi Map
Wifi Map creation with ForceGraph…
Each Wifi scan creates one ForceNode(type=ROUTE), and each new access point from scan results creates new ForceNode(type=WIFI). Each ForceNode(type=WIFI) is connected to ForceNode(type=ROUTE) with ForceRelation, which target length is set to estimated distance to Wifi access point.
When application is scanning more Wifi access points, ForceGraph build up so that basically every ForceNode(type=WIFI) is connected to many different ForceNode(type=ROUTE).
Now when ForceGraph is continuously iterating new locations to each ForceNode, locations of Wifi access points and routes are finding their actual locations.
